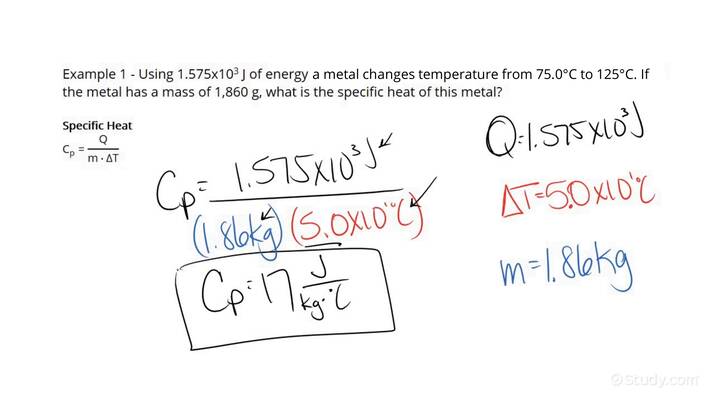
Smart Ways to Calculate Specific Heat in 2025: Essential Methods and Tips
Smart Ways to Calculate Specific Heat in 2025
Understanding specific heat is fundamental to various scientific fields, including chemistry and physics. Knowing how to calculate specific heat accurately can enhance your understanding of thermal energy, heat transfer, and material properties. In this article, we will explore effective methods and innovative tips for determining specific heat, along with practical applications to illuminate this crucial concept.
Understanding Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity defines how much heat energy is required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius. It’s a critical concept in calorimetry and essential for studying thermodynamics. Different materials have varying specific heat values, which means they absorb and release heat at different rates. For example, water’s specific heat is notably high at around 4.18 J/g°C, allowing it to store energy efficiently.
The Specific Heat Formula
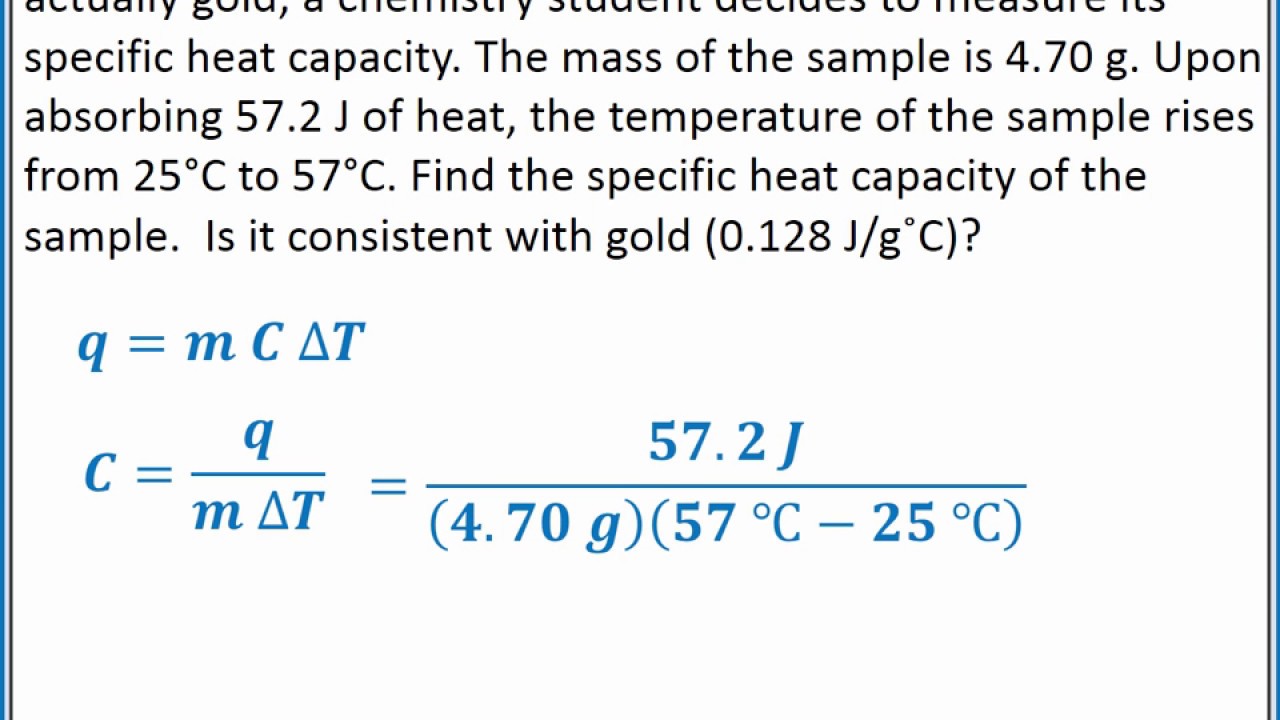
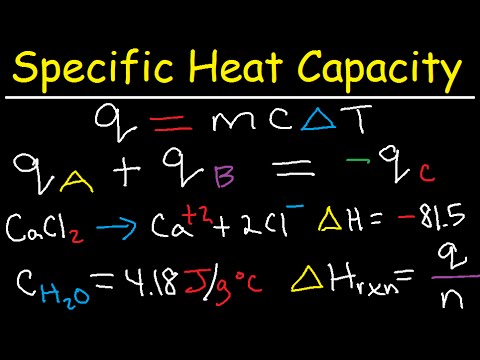
The specific heat formula is given by the equation:
Q = mcΔT, where Q is the heat energy absorbed or released, m is the mass of the substance, c is the specific heat capacity, and ΔT is the temperature change. This equation enables calculation of the specific heat when the amount of heat transferred and the resulting temperature change are known. For instance, in practical applications like cooking, knowing the specific heat of ingredients can influence how they cook and retain heat.
Units of Specific Heat
Specific heat is expressed in various units of specific heat, with the most common being Joules per gram per degree Celsius (J/g°C) or calories per gram per degree Celsius (cal/g°C). When performing specific heat calculations, it’s paramount to match the units. Conversions may be necessary, especially when applying different measuring systems (SI vs. imperial), to ensure accuracy in calculations. By standardizing measurements, you can easily compare the thermal properties of different materials.
Examples of Specific Heat Values
<pThere are different types of materials with their respective specific heat values:
- Water: approximately 4.18 J/g°C
- Ice: about 2.09 J/g°C
- Iron: around 0.45 J/g°C
- Aluminum: roughly 0.90 J/g°C
These specific heat variations highlight how diverse materials respond to heat. In practical applications, the specific heat value of a material can significantly affect energy use and efficiency in processes like heating, cooling, and insulation.
Methods to Determine Specific Heat
There are several methods to determine specific heat, each appropriate for specific scenarios in education or industrial applications. Here, we explore some common methods:
Calorimetry Experiments
Calorimetry is a laboratory technique utilized to measure heat transfer during chemical reactions or changes of state. In a common calorimetry experiment, a known mass of water is heated, and the temperature change is monitored. By rearranging the specific heat equation to isolate ‘c’, researchers can derive the specific heat of an unknown substance by analyzing its effects during the temperature changes of the water. Students often conduct this experiment in class, providing hands-on experience with scientific principles and accurate data gathering.
Specific Heat Lab Guidelines
When performing a supply heat-specific heat lab experiment, accuracy in measurement is critical. Students are encouraged to use calibrated thermometers and accurate scales to record mass and temperature changes meticulously. The safety considerations for heating materials in the lab should also be reviewed; precise techniques dictate successful results. It’s also beneficial to maintain thermal equilibrium to reduce measurement errors.
Online Calculators for Specific Heat
Numerous online calculators simplify calculating specific heat. By inputting mass, heat absorbed, and temperature changes, users can find specific heat without manually manipulating formulas. These tools serve helpful for quick determinations in both educational and professional settings. Using such calculators, however, must still involve an understanding of thermodynamic principles to interpret results accurately and confirm that calculated values reflect the material characteristics.
Common Applications of Specific Heat
Understanding specific heat helps in various real-world applications, influencing numerous scientific and engineering fields. Here are some primary applications and why they matter:
Specific Heat in Engineering
In engineering, specific heat plays a vital role in thermal management. It’s crucial in designing systems related to energy efficiency and heat exchange, especially in HVAC applications. Engineers use specific heat values to predict how materials react to thermal loads, determining suitable materials and designs to optimize energy use and reduce costs effectively. Being equipped with knowledge regarding specific heat in engineering can lead to significant advancements in sustainable practices.
Role of Specific Heat in Climate Science
The understanding of specific heat dynamics significantly influences climate science. For instance, water bodies’ high specific heat capacity stabilizes temperature, impacting weather patterns and climate regulation. This concept also aids scientists in modeling climate change effects and predicting future scenarios. Hence, it’s essential to grasp the role of specific heat in climate for broader discussions in scientific communities and policymakers.
Significance in Everyday Cooking
When cooking, understanding the specific heat of materials, like metals, water, and oils, enlightens our ability to prepare food efficiently. Different cooking methods utilize these assets, controlling heat environments to achieve the desired cooking results. Whether for baking or frying, knowing specific heat values allows cooks to optimize processes, enhancing flavors and textures in food preparation.
Key Takeaways
- Specific heat capacity measures the energy required to change a substance’s temperature.
- The specific heat formula is fundamental in heat transfer calculations.
- Methods for measuring specific heat include calorimetry, laboratory experiments, and the use of online calculators.
- Specific heat has impactful applications in engineering, climate science, and everyday cooking.
FAQ
1. What is the specific heat definition?
The specific heat definition refers to the amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. It varies across different materials and is integral in various scientific calculations related to thermal energy.
2. How does specific heat affect temperature change?
Specific heat influences how quickly a substance can change temperature when heat energy is added or removed. Materials with high specific heat, like water, will warm up slowly compared to those with lower specific heat, allowing heat absorption without drastic temperature changes.
3. What are common materials with specific heat variations?
Common materials exhibit variable specific heat values. Water has a high specific heat (4.18 J/g°C), while metals like iron and aluminum have significantly lower values, around 0.45 J/g°C and 0.90 J/g°C respectively. Understanding these variations aids in practical applications in cooking, cooling systems, and material choice.
4. How can I estimate specific heat using water?
To estimate specific heat using water, a popular experimental technique is calorimetry. By measuring the temperature change of water caused by an object’s heat exchange, the specific heat of that object can be calculated using the specific heat formula, considering energy balance principles.
5. Why is specific heat significant in environmental science?
Specific heat is significant in environmental science as it influences climate models and ecological systems. Water’s capacity to moderate temperatures is vital for maintaining stable ecosystems and understanding weather patterns, thus emphasizing its importance in climate studies.
6. Can I calculate specific heat online?
Yes, online platforms provide calculators where users input required values like mass, heat added, and temperature change to find specific heat. Utilizing these tools can expedite calculations, making scientific assessments more accessible and time-efficient.
7. What role does specific heat play in cooking?
In cooking, knowing the specific heat of materials helps chefs control cooking times and temperatures effectively. Understanding how different foods retain or lose heat informs cooking strategies, enhancing food quality and safety.