Essential Guide to How to Calculate Operating Income in 2025 – Discover Key Methods and Tips
Essential Guide to How to Calculate Operating Income in 2025
Calculating operating income is crucial for analyzing a company’s financial performance. Understanding how to compute this key metric helps ascertain profitability and aids in decision-making processes. This guide delves into the **operating income** concept, explains the formula, outlines methods of calculation, and offers valuable tips for effective financial statement analysis. Whether you’re a business owner or involved in management accounting, mastering this skill can enhance your ability to define and assess profitability.
Understanding Operating Income and Its Importance
**Operating income** refers to the profit realized from a company’s core business operations. Unlike net income, which includes all revenues and expenses, operating income focuses specifically on the revenues generated from operations minus directly related operating expenses. This distinction makes it an essential metric for assessing a business’s profitability. In 2025, understanding **operating income** is better than ever due to evolving financial landscapes where detailed profitability analysis is paramount. Analyzing operating income aids businesses in several areas, such as managing **fixed costs**, controlling **variable costs**, and optimizing **operating profit margins**.
The Definition of Operating Income
Operating income is fundamentally considered an **income statement line item** that highlights the effectiveness of a company in generating profit from its normal operations. To arrive at operating income, one must focus on revenue calculation that includes sales minus the **operating expenses** associated with generating that revenue. Typically, companies aim for a higher operating income, reflecting efficient management of both direct costs and indirect costs.
Key Components: Revenue and Expenses
To calculate operating income, an understanding of the principal components: **revenue generation** and **expense deduction** is crucial. Revenue is generated from sales, while expenses might include rent, salaries, utility costs, and materials. Effectively managing these elements contributes to maximizing operating income. Recognizing which costs are **fixed** (such as rent) and which are **variable** (such as electricity) helps businesses create effective **cost management** strategies and forecast future profitability.
Operating Income in Financial Statement Analysis
In financial statement **analysis**, operating income serves as a vital metric in determining operational efficiency. Investors and analysts often look for trends in operating income over time or compare it against **financial metrics** from similar companies within the industry. Operating income not only highlights a company’s profitability before interest and taxes but also serves as a foundation for ratio analysis, facilitating deeper insights into performance indicators.
Calculating Operating Income: The Formula
The formula for calculating operating income is straightforward yet provides significant insights into financial health. The basic **operating income formula** is:
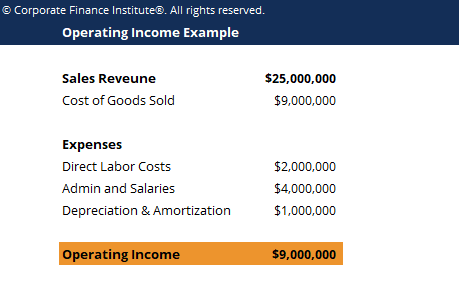
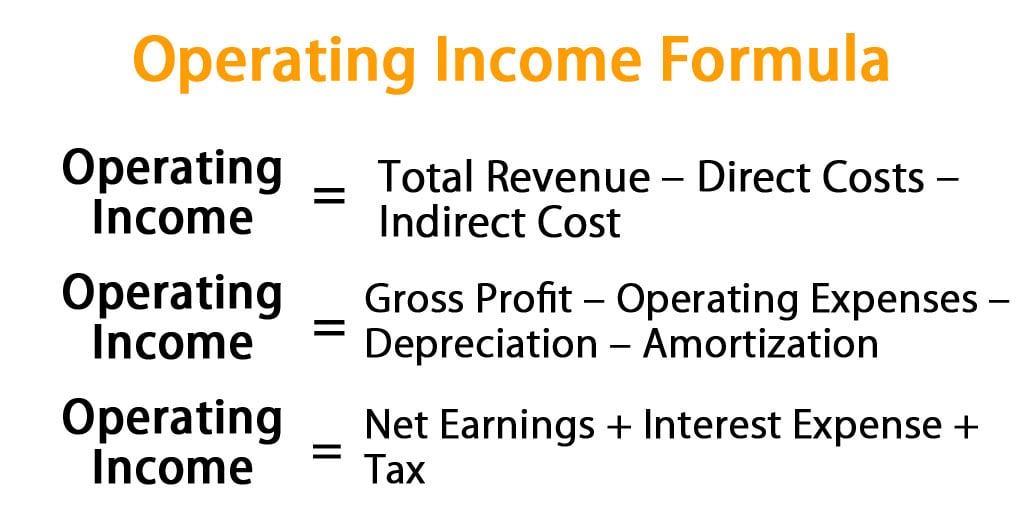
Operating Income = Gross Income – Operating Expenses
Breaking this down, gross income is derived from total revenues minus cost of goods sold (COGS), while operating expenses encompass all overhead and other operational costs drawn from **fixed costs** and **variable costs**. Understanding this formula allows you to isolate and evaluate business activities that generate income effectively.
Example of Operating Income Calculation
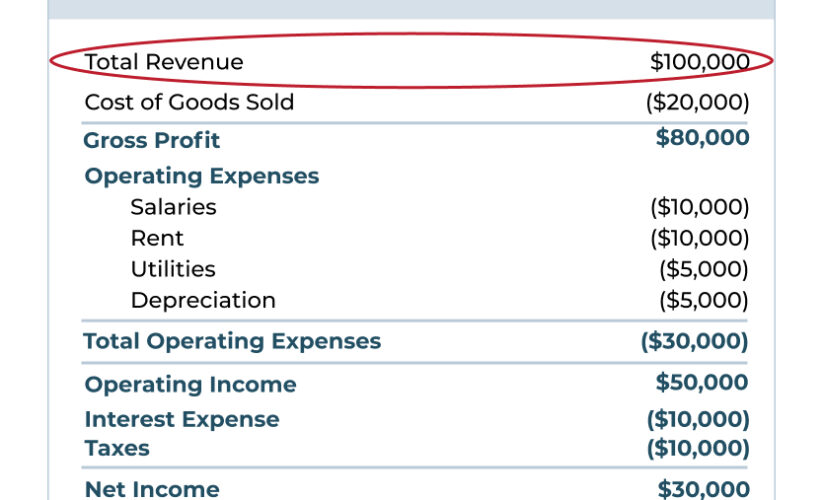
To illustrate the operating income calculation, consider a fictional company, ABC Corp., that has the following data for the year:
- Total Revenue: $500,000
- COGS: $300,000
- Administrative Expenses: $100,000
- Marketing Expenses: $50,000
First, calculate Gross Income:
Gross Income = Total Revenue – COGS
Gross Income = $500,000 – $300,000 = $200,000
Next, sum the Operating Expenses:
Operating Expenses = Admin Expenses + Marketing Expenses = $100,000 + $50,000 = $150,000
Now, we can find the Operating Income:
Operating Income = Gross Income – Operating Expenses
Operating Income = $200,000 – $150,000 = $50,000
This example showcases the step-by-step approach to **operating profit calculation**, emphasizing the importance of tracking revenues and expenses accurately.
Potential Pitfalls in Operating Income Calculation
When calculating operating income, some common pitfalls involve misclassifying revenue or expenses, ignoring one-time costs, or failing to delineate between direct and indirect costs. For accurate evaluations in **financial reporting**, ensuring that all costs associated directly with revenue generation are accounted for is crucial. Consistently applying accounting principles can improve the reliability of operating income figures and thus enhance performance evaluation.
Tips for Optimizing Operating Income Calculation
To optimize the process of calculating operating income, consider the following steps:
- Implement Management Accounting Techniques: Use advanced management accounting techniques to gain insights into cost behaviors affecting overall profitability.
- Utilize Financial Performance Indicators: Keep track of profitability ratios that provide context to your operating income, guiding strategic decision-making.
- Engage in Regular Financial Audits: Conducting regular audits can help minimize discrepancies in income calculations and enhance operating efficiency, ensuring you don’t overlook critical performance data.
- Focus on Understanding Cost Structures: Analyzing the company’s **cost structure** and making informed **pricing strategies** can lead to better management of both fixed and variable expenses.
Integrating EBITDA for Depth in Analysis
Although often used interchangeably with operating income, EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) encompasses additional elements that provide even deeper insights into the business’s financial standing. By incorporating EBITDA in conjunction with your operating income, you can gain a clearer picture of your operational profitability, which is particularly helpful for **business valuation methods** and **investment analysis**.
Benchmarking and Industry Norms
Another effective technique for evaluating and optimizing operating income is through benchmarking – comparing your company’s operating income with industry standards or competitors. This practice can identify areas for improvement and help refine **business profitability** strategies by assessing where you rank against peers in essential **financial metrics**.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding **operating income** is crucial for comprehensive financial assessment and profitability analysis.
- Accurate calculations of operating income utilize a clear formula of gross income minus operating expenses.
- Regular audits and a keen focus on **cost management** can significantly improve operating income.
- Comparative analyses through **benchmarking** can offer critical insights into how to enhance efficiencies.
FAQ
1. What is the primary significance of operating income in financial analysis?
Operating income reveals how well a company utilizes its resources to produce profit directly from its operational activities. By focusing specifically on profits generated from core business, analysts can evaluate company performance more accurately, disregarding financing and incidental income factors.
2. How often should a company recalculate its operating income?
Companies should recalculate their operating income regularly, ideally at the end of every fiscal quarter or month. This timeframe allows businesses to monitor profitability trends and engage in effective **financial planning**.
3. What differences exist between operating income and net income?
While both operating income and net income measure profitability, operating income includes only revenues and expenses directly associated with operations. In contrast, net income accounts for all revenues, including non-operating income or expenses, making it a broader measure of overall profitability.
4. Can variations in fixed costs significantly impact operating income?
Absolutely. Variations in fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, can have a profound impact on operating income, particularly if a business has lower sales volume. Monitoring and controlling these costs are essential for maintaining healthy margins.
5. What role does operating income play in profitability analysis?
Operating income serves as a key performance indicator (KPI) for assessing profitability. By analyzing operating income relative to revenue, businesses can evaluate their operational efficiency, which is crucial for **profit optimization** and strategic decision-making.
6. How do changes in pricing strategies affect operating income?
Changes in pricing strategies can directly affect operating income by either increasing or decreasing revenue. A thoughtful pricing strategy aligned with market demands can boost sales volume, enhancing revenue and, consequently, operating income.
7. What are some common mistakes in calculating operating income?
Common mistakes include misrecording **operating expenses** as non-operating costs, neglecting to account for all necessary direct costs, or overlooking ongoing expenses, all of which can distort the perceived profitability of the business.
—
Enhancing an understanding of operating income provides tools for monitoring financial health and maximizing profitability. By applying the methods and insights discussed in this article, individuals and businesses can significantly improve their financial outcomes, supporting future growth and stability.