Complete Guide to Finding the Surface Area of 3D Shapes in 2025: Learn More!
“`html
Complete Guide to Finding the Surface Area of 3D Shapes in 2025: Learn More!
Understanding how to find surface area is essential for various applications in mathematics, science, and engineering. In 2025, the approach to calculate surface area has evolved, integrating new teaching methodologies and technology. This guide will provide comprehensive insights into surface area formulas, practical uses, and techniques for finding surface area of a shape.
Key Surface Area Concepts
Understanding basic surface area concepts is crucial before delving into specific formulas and calculations. Each 3D shape, from the surface area of a cube to the surface area of a cylinder, has unique properties that guide calculations.
Surface Area Formulas for Common Shapes
The formula for surface area varies among different shapes. Here’s a brief overview for some common 3D shapes:
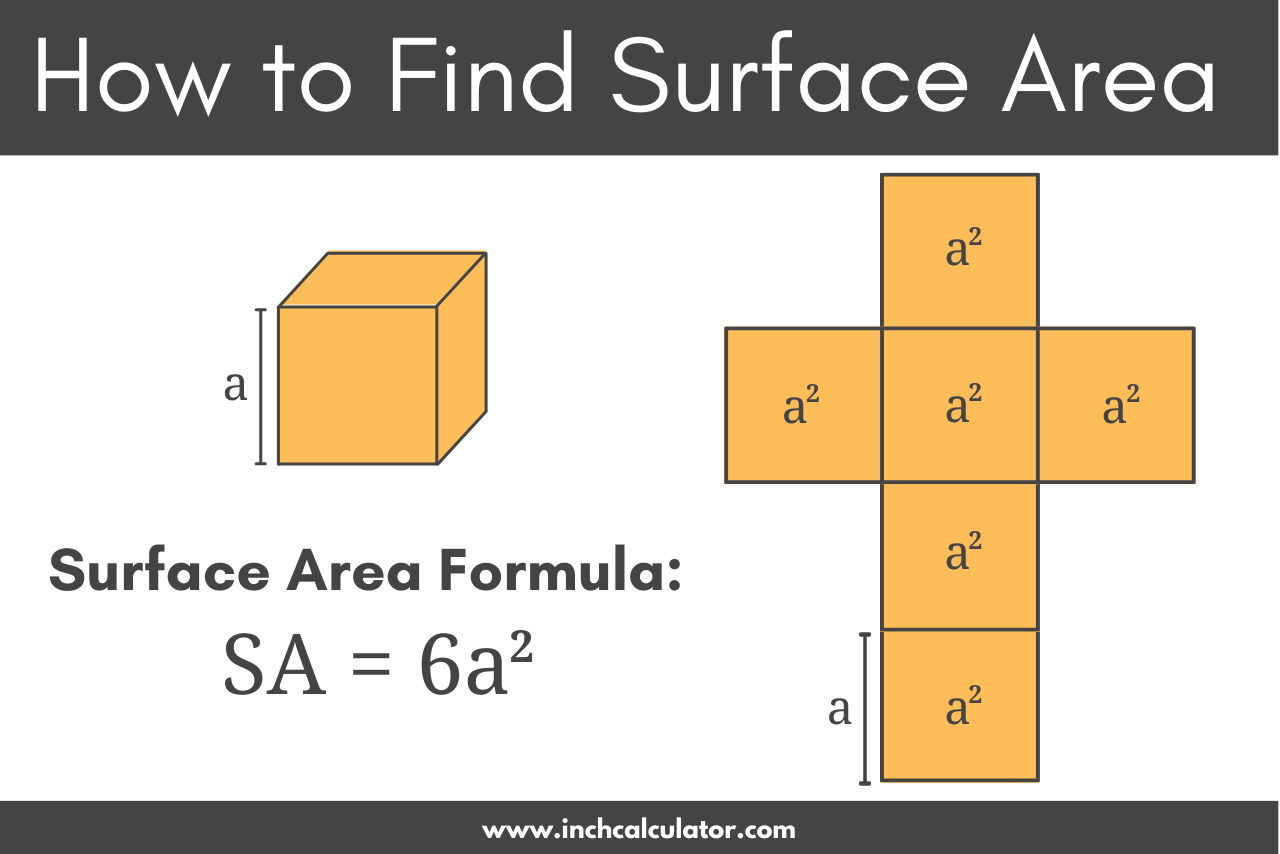
- Cube: Each face is a square. The formula is 6a², where ‘a’ is the length of a side.
- Cylinder: The formula is 2πr(h + r), where ‘r’ is the radius and ‘h’ is the height.
- Sphere: The formula is 4πr².
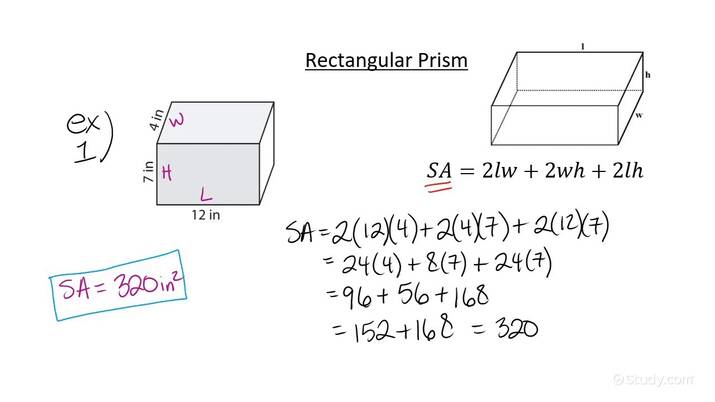
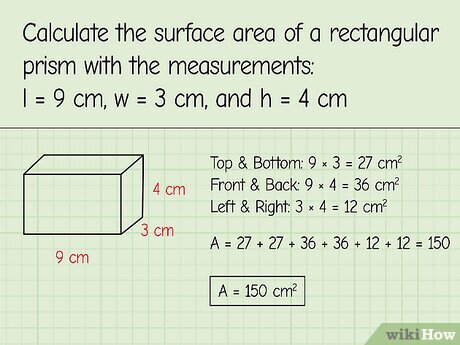
- Rectangular Prism: The formula is 2(lw + lh + wh), where ‘l’, ‘w’, and ‘h’ are the length, width, and height respectively.
- Pyramid: The surface area depends on the base shape, typically calculated as the base area plus the area of the sides.
Surface Area of Irregular Shapes
Finding surface area of irregular shapes can be challenging. One common technique is to break the shape down into regular components, calculate each area, and then sum them up. Alternatively, advanced methods may use calculus for continuous shapes. Understanding these techniques allows for a comprehensive approach to surface area calculations.
Practical Applications of Surface Area
The relevance of surface area in real life is multi-faceted, impacting several fields from architecture to biology. Knowing how to measure surface area allows professionals to optimize design and functionality in various applications.
Surface Area in Engineering and Architecture
The measurement of surface area holds significant importance in engineering and architecture. In engineering, achieving the right surface area can ensure structures are stable and durable. In architecture, understanding surface area impacts design principles, contributing to energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal.
Practical Example: Energy Efficiency in Buildings
For instance, in building design, the ratio of surface area to volume influences energy consumption. A building with a lower surface area relative to its volume will require less energy for heating, cooling, and ventilation. This understanding leads to sustainable architecture, directly impacting environmental conservation efforts.
Surface Area in Biology and Chemistry
Surface area also plays a vital role in biological and chemical processes. For example, cells maximize their surface area to enhance nutrient absorption. Similarly, in chemistry, reactions occur at surfaces, where greater surface area leads to higher rates of reaction. This connection shows the significance of surface area applications across scientific disciplines.
Techniques for Calculating Surface Area
Various methods for calculating surface area are essential for accurate measurement and education. Utilizing tools like surface area calculators or engaging in hands-on activities can support understanding.
Online Tools and Software
In today’s digital age, online surface area tools and calculators simplify the process of calculating surface area. By inputting dimensions, users can quickly derive the surface area for various shapes. These tools are invaluable for students and professionals alike.
Hands-On Surface Area Activities
Encouraging tactile learning through hands-on surface area activities can enhance comprehension. For example, using everyday objects like boxes and balls, students can physically measure dimensions and apply formulas, thereby bolstering their understanding of how to measure surface area effectively.
Visual Aids in Teaching Surface Area Concepts
Integrating graphic representations of surface area can aid in visual learners’ understanding. Diagrams, charts, and models help illustrate how to find surface area, making abstract concepts more tangible. Utilizing such resources can greatly enhance instructional effectiveness in a classroom or self-study environment.
Summary and Key Takeaways
Understanding surface area is pivotal in many domains. Key aspects include:
- Mastery of surface area formulas for various 3D shapes.
- Recognition of the real-life applications of surface area, from engineering to biology.
- Utilization of modern tools and hands-on techniques to improve learning outcomes.
FAQ
1. What is the definition of surface area?
The surface area definition refers to the total area that the surface of a three-dimensional object occupies. It is crucial for determining the amount of material needed for construction, the exposure of a substance in reactions, and more.
2. How can I calculate the surface area of a triangular prism?
To find the surface area of a triangular prism, calculate the area of the two triangular bases and the three rectangular faces. The formula is A = bh + 3lw (where ‘b’ is the base, ‘h’ is the height, and ‘l’ is the length of the prism).
3. Why is surface area important in science?
In science, surface area affects reaction rates in chemistry and nutrient absorption in biology. A larger surface area can lead to faster reactions and more efficient processes in living organisms.
4. What are some common mistakes in surface area calculations?
Common mistakes include incorrect interpretations of dimensions, confusing units of measurements, or neglecting to include all surfaces, especially in complex shapes. Paying close attention to dimensions and formulas will help prevent these errors.
5. How do I find the surface area of irregular shapes?
Finding the surface area of irregular shapes often requires breaking the shape into manageable parts, calculating their areas individually, and summing them up. Advanced methods might also involve calculus or digital tools for more complex figures.
“`