How to Effectively Calculate Price Elasticity of Demand in 2025: Discover Proven Methods to Optimize Your Business!
How to Effectively Calculate Price Elasticity of Demand in 2025
Understanding the price elasticity of demand is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their pricing strategies in 2025. By accurately assessing how the demand for a product changes with varying prices, businesses can make data-driven decisions that enhance profitability and market share. This article explores proven methods and practical tips to effectively calculate price elasticity, providing insights into its implications for your business strategy.
Understanding Elasticity and Its Importance
Elasticity is a key concept in economics that measures how sensitive the quantity demanded of a good is to changes in price. The demand elasticity formula provides a calculated figure based on percentage changes in price and quantity demanded. Understanding elasticity is vital as it helps businesses evaluate how price changes can impact demand. For example, knowing whether a product exhibits elastic demand or inelastic demand enables marketers to tailor their pricing strategies effectively.
What Is Price Elasticity of Demand?
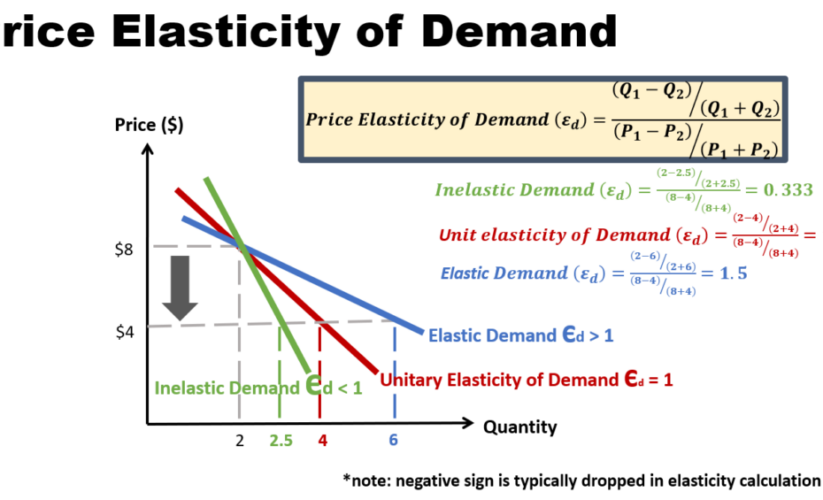
The price elasticity of demand quantifies the response of consumers to price changes, expressed as a ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded to the percentage change in price. If elasticity is greater than one, the demand is considered elastic; if less than one, it is inelastic. This measurement helps businesses assess how a price change will affect their total revenue. For instance, a price sensitivity analysis can be performed to evaluate how much price variations affect consumer behavior and spending habits, ultimately impacting sales projections.
Determinants of Elasticity
Several factors influence how elastic or inelastic a product’s demand is. Key determinants include the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the product, and the proportion of income spent on the good. Luxury goods tend to have higher elasticity compared to necessity items. An understanding of these factors affecting elasticity allows businesses to predict how changes in market conditions will affect demand. Companies should regularly approach elasticity measurement techniques to adapt their strategies as consumer preferences and economic environments shift.
Interpreting Elasticity Values
Interpreting elasticity involves understanding what different values mean for your business’s bottom line. An elastic value indicates that a small change in price can lead to a significant change in quantity demanded, whereas an inelastic value suggests minimal impact on demand. Businesses can use the total revenue test to determine the relationship between price changes and total revenue, reinforcing the importance of applying elasticity in pricing models strategically.
Calculating Price Elasticity Using Various Methods
Calculating price elasticity accurately requires the application of different methods depending on the data available and the specific market conditions. Here, we explore the most effective calculation methods for price elasticity.
Calculating Midpoint Elasticity
The midpoint elasticity method is a practical calculation technique that averages the initial and new price and quantity. This formula avoids the discrepancies incurred by percentage calculations and provides a more accurate elasticity measure. Businesses can apply this method by using the following formula:
Elasticity = (Q2 – Q1) / [(Q2 + Q1)/2] ÷ (P2 – P1) / [(P2 + P1)/2].
This approach is particularly effective in scenarios with significant price changes, providing nuanced insights into how price effects on demand manifest over time.
Point Elasticity vs Arc Elasticity
When discussing elasticity, understanding the difference between point elasticity and arc elasticity is essential. Point elasticity measures the elasticity at a specific point on the demand curve, while arc elasticity assesses changes between two distinct points. Utilizing the proper method for calculating elasticity of demand can dramatically influence business strategies and forecasts. For instance, firms may opt for arc elasticity over point elasticity when analyzing broader consumer behavior trends across multiple price points.
Employing Statistical Analysis and Data Analytics Tools
In today’s data-driven economy, businesses can leverage advanced analytics tools that implement complex statistical models to refine their elasticity calculations. Employing big data and machine learning algorithms improves forecasting accuracy. By analyzing historical data on pricing and demand responses, companies can better predict how their adjustments will impact consumer behavior. This approach is particularly beneficial for understanding market trends and making proactive business decisions.
Real-World Applications of Price Elasticity of Demand
Understanding and implementing price elasticity of demand can have significant implications for marketing strategies and overall business performance. Let’s examine how to meaningfully apply elasticity concepts in real-world scenarios.
Price Elasticity in Marketing Strategies
The intersection of price elasticity and marketing strategy is critical. By understanding consumer behavior and demand responsiveness, businesses can create effective marketing campaigns that reflect the anticipated reaction to price changes. For example, targeted promotions and discounts can capitalize on elasticity insights to drive higher sales volumes in price elastic markets, ensuring that short-term revenue maximization aligns with long-term brand strategy.
Elasticity and Total Expenditure
Exploring the relationship between elasticity and total expenditure provides valuable insights. If a product’s demand is elastic, a price decrease may lead to increased expenditure as consumers buy more. Conversely, for inelastic goods, a price increase may not significantly affect total expenditures since consumers continue purchasing despite the price hike. Businesses should monitor these dynamics closely, particularly during several economic cycles, to adjust their pricing strategies appropriately.
Factors Influencing Demand Shifts and Elasticity
Various external factors can cause demand shifts that influence elasticity. Changes in consumer preferences, income levels, and external economic conditions can all affect how responsive demand is to price changes. Businesses must remain sensitive to these factors and continuously analyze data to adjust their pricing and marketing strategies accordingly. Keeping an eye on demand shift factors helps in creating agile business models capable of enduring market fluctuations and consumer preference changes.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding price elasticity of demand is vital for optimizing pricing strategies.
- Different methods, like midpoint and arc elasticity, provide valuable insights into how demand responds to price changes.
- Employing statistical analysis and predictive tools strengthens the accuracy of elasticity calculations.
- The connection between elasticity and total expenditure can inform effective marketing strategies.
- Awareness of demand shift factors enables agile adjustments to business strategies.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand?
Elastic demand</ refers to situations where a small change in price leads to a significant change in quantity demanded, while inelastic demand indicates that quantity demanded remains relatively unchanged despite price variations. Understanding these differences helps businesses shape their pricing strategies effectively.
2. How do seasonal changes affect price elasticity?
Seasonal variations can lead to changes in demand elasticity. For instance, holiday seasons may increase demand for certain products, making them more elastic, while products such as basic food items generally maintain inelastic characteristics throughout the year. Businesses must analyze these seasonal trends to adjust their sales tactics accordingly.
3. What role does consumer income play in demand elasticity?
Increasing consumer income often leads to changes in elasticity across products. As income rises, the demand for luxury goods may become more elastic, as consumers have greater flexibility to respond to price changes. Conversely, basic necessity items remain typically inelastic. Businesses should consider income trends when forecasting demand.
4. How can I calculate elasticity using historical data?
To calculate elasticity using data, start with obtaining historical prices and corresponding quantities sold. Then apply the appropriate formula—be it midpoint, point, or arc elasticity—to determine the responsiveness of demand. Statistical software can enhance the accuracy by analyzing larger datasets over time.
5. Can marketing strategies leverage knowledge of elasticity?
Absolutely! Leveraging knowledge of price sensitivity allows businesses to devise targeted marketing campaigns that can either promote price reductions in elastic markets or maintain prices in inelastic markets. This kind of strategic approach can maximize sales while minimizing losses during price fluctuations.
6. How is elasticity relevant in international trade?
In international trade, elasticity becomes a vital tool for understanding how foreign markets will respond to trade decisions, tariffs, or price changes. Different economic conditions and cultural factors in international markets can greatly affect demand responsiveness, guiding companies in their export and pricing strategies.
7. What technologies can help with elasticity calculations?
Utilizing advanced analytics, machine learning algorithms, and econometric modeling software can significantly improve the processes for calculating elasticity. These technologies assist in dissecting complex datasets effectively, leading to more reliable elasticity estimations that can positively influence decision-making processes.